Microplastics discovered in new deep sea species
scuba divingenvironmentmarine lifeoceanconservationpollution
1 views - 1 viewers (visible to dev)

Eurythenes plasticus (c) WWF Deutschland
Researchers officially name flea cancer "Plasticus" Only five centimetres tall, its home in about 6,500 meters depth in the Pacific Ocean and it still has plastic in its body: Eurythenes plasticus. The newly discovered deep-sea species is a species of amphipod that researchers at Newcastle University have found in the Mariana Trench near the Philippines, near one of the deepest points on earth. "Eurythenes plasticus" was named by the head of the research mission, Dr. Alan Jamieson. "With the name we want to send a strong signal against marine pollution and make it clear that we urgently need to do something about the massive plastic flood," comments Jamieson. With the support of WWF Germany, the scientists around Jamieson have now published the results of the research in the renowned journal Zootaxa. "The newly discovered species Eurythenes plasticus shows how far-reaching the consequences of our lax handling of plastic are. There are species that live in the deepest and most remote parts of our planet and are nevertheless heavily contaminated with plastic. Plastic is in the air we breathe, the water we drink and the animals that live far from human civilization," comments Heike Vesper, director of the WWF Center for Marine Protection. In the amphipod, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) was found, a substance that is found in many everyday objects such as disposable drinking bottles and sportswear. "The plastic crisis affects us all, because we all use PET in everyday life," says Vesper. The path of plastic from human use in animals like E. plasticus is long. Germany is the world's third largest exporter of plastic waste after the United States and Japan. Plastic waste often ends up with poor or no waste management in Southeast Asian countries. There it can often not be recycled, but is burned or ends up in landfills - and also gets into the sea from there. In the water, the plastic waste is broken up into microplastics, distributed and taken up by animals such as E. Plasticus. "To stop the global plastic flood, a global solution is needed. The WWF is therefore committed to an international agreement that will legally prescribe waste reduction and improved waste management worldwide," said Vesper. "Not all specimens of the new species E. plasticus found, already had plastic in their bodies. So there is still hope that other specimens of the species will not live up to their name and that they will remain plastic-free." To do this, however, politicians must make efforts to avoid plastics. Background The plastic PET found in amphipod is used, among other things, to manufacture disposable drinking bottles, foils and textile fibers. In the sea, PET and other plastics can combine with industrial and chemical pollutants that degrade very slowly in the environment. Microplastic particles easily get into the bodies of marine animals. The concrete effects of this have not yet been sufficiently researched. But one thing is clear: plastic often also contains additives such as plasticizers and flame retardants, which harm the marine life and can also reach people through the food chain.
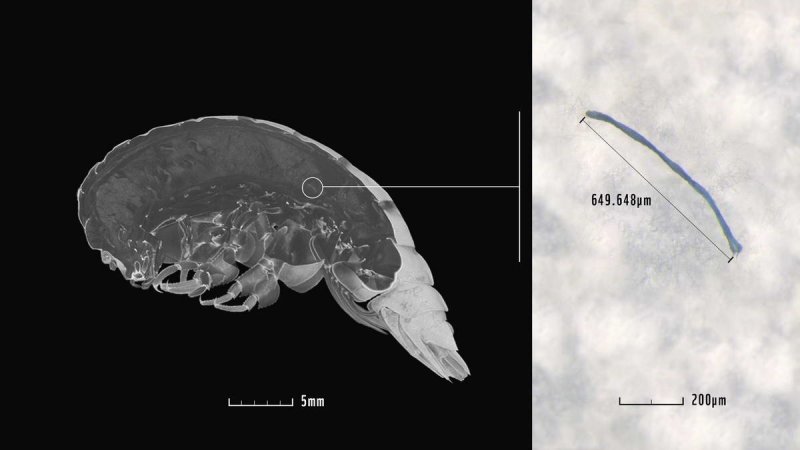
Eurythenes plasticus (c) WWF Deutschland

Eurythenes plasticus (c) WWF Deutschland
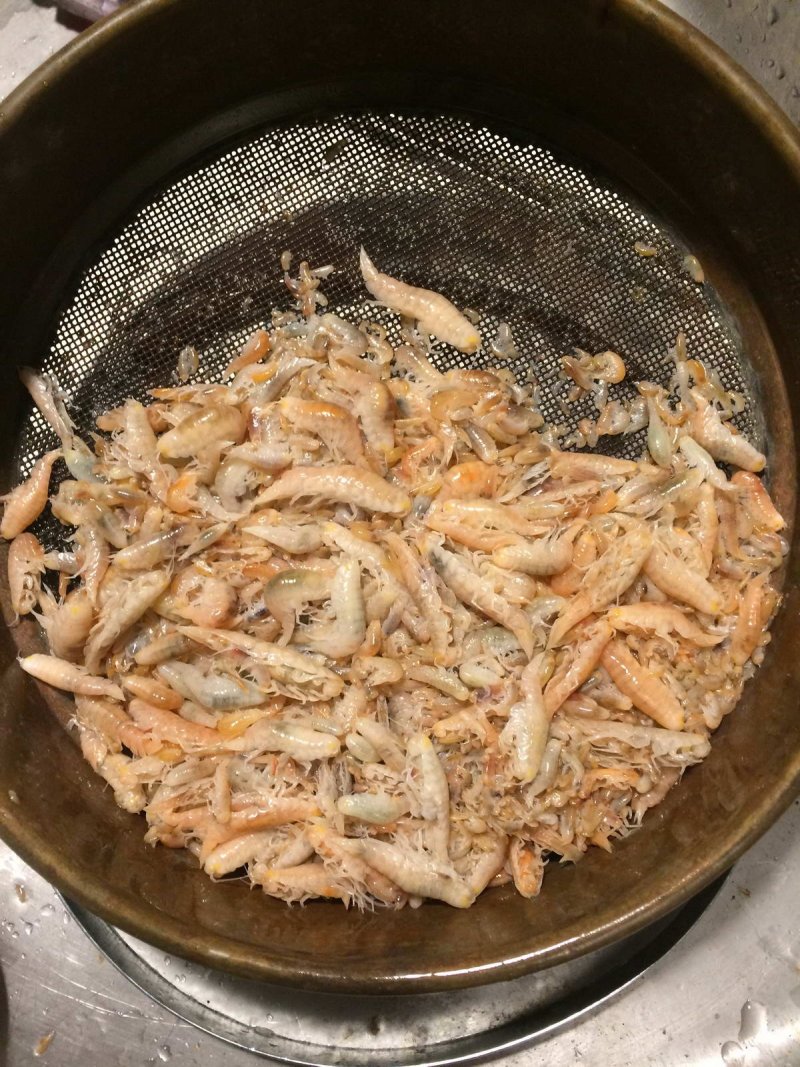

Eurythenes plasticus (c) WWF Deutschland
本文為自動翻譯,可能包含些微不準確之處;如有疑問,請以英文原文為準。