In the focus: The oceans most productive areas
environmentclimate changebiodiversitymarine researchocean currents
0 views - 0 viewers (visible to dev)

As early as 2017, the mesocosms were deployed off the coast of Peru,(c) Ulf Riebesell / GEOMAR
Researchers are investigating upwelling areas off Africa and South America On the eastern edges of the Atlantic and the Pacific, continuous buoyancy of nutrient-rich deep water provides extremely high biological productivity. However, how these upwelling areas develop when wind systems shift due to climate change and the ocean gradually warms up is largely unclear. Three collaborative projects will address these issues over the next three years. The overall coordination lies with the GEOMAR Helmholtz Center for Ocean Research Kiel Although they occupy just fewer than two percent of the surface of the oceans, the large coastal upwelling areas on the eastern edges of the Pacific and the Atlantic are among the most biologically productive marine areas of all. Not only do they have a large biodiversity, they also provide 20 percent of the world's fishery contributions. Therefore, these regions also have enormous significance for the society and economy of the neighbouring countries as well as for the entire world food supply. But can they still fulfil this function if the oceans continue to warm, become more acidic, continue to lose oxygen, and possibly change wind systems over the sea? Starting in January 2019, the Federal Ministry of Research will sponsor three joint projects under the theme "Importance of climate change in coastal upwelling areas", which will deal intensively with the coastal upwelling areas in the northeast and southeast Atlantic as well as in the south-eastern Pacific. Two of these projects as well as cross-community activities are coordinated at GEOMAR. " The aim is to better understand the sensitivity of these areas to climate change in order to identify possible consequences at an early stage, " explains Prof. Dr. med. Ulf Riebesell, overall coordinator of the main topic. The coastal upwelling areas are all in the range of large, parallel to the coast running ocean currents. In the southeast Atlantic this is the Benguelastrom, in the northeast Atlantic the Canary Current and in the Southeast Pacific the Humboldt Current. Trade winds drive the water masses towards the equator. The Earth's rotation ensures that near-surface water moves away from the coast. This draws cold, nutrient-rich water from the depths to the surface, thus driving biological production. One of the two joint projects coordinated by GEOMAR is called REEBUS (role of vortices for the carbon pump in coastal upwelling areas). " It is based on the observation that oceanic vortices play a central role in the physical, biogeochemical and biological properties of coastal upwelling areas, " explains REEBUS coordinator Prof. Dr. med. Arne Körtzinger from GEOMAR. The researchers want to better understand vertebrae with a novel, multi-layered observation approach and with the help of process models. The REEBUS team can rely on preparatory work by the Kiel Collaborative Research Center 754. " Fortunately, with the Ocean Science Center Mindelo on the Cape Verde Islands, we have a modern base for the planned field work in the area of the coastal upwelling area off West Africa, " emphasizes Körtzinger. The centrepiece is three GEOMAR-led research expeditions in 2019 and 2020. The second joint project CUSCO (Coastal Upwelling System in a Changing Ocean) coordinated by GEOMAR focuses above all on the upwelling area off Peru in the Humboldt Current. " Although it is the most productive of all coastal upwelling areas, it is completely unclear how biological productivity is related to the intensity of buoyancy. We want to understand better how this highly productive ecosystem reacts when the uplift caused by climate change changes, " says Professor Riebesell, who also coordinates CUSCO. CUSCO relies mainly on an expedition with the German research vessel "MARIA S. MERIAN", which has been carried out since December 2018 off the coast of Peru. Another important building block is an experiment with the Kiel offshore mesocosms pilot plant KOSMOS from February to April 2020 in the coastal waters of Peru. In addition, there are computer simulations on different scales from specially adapted ecosystem models to regional simulations of the physical and biogeochemical processes. Together with REEBUS and CUSCO, this is started by Prof. Dr. med. Heide Schulz-Vogt of the Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research in Warnemünde (IOW) coordinated project EVAR, which focuses primarily on investigations in the buoyancy system of the Benguela River.

The upwelling area in the Humboldt Current off the coast of Peru is one of the most productive in the world. With the help of the Kiel offshore mesocosms pilot plant KOSMOS, new insights into its functioning are to be gained, (c) Ulf Riebesell / GEOMAR
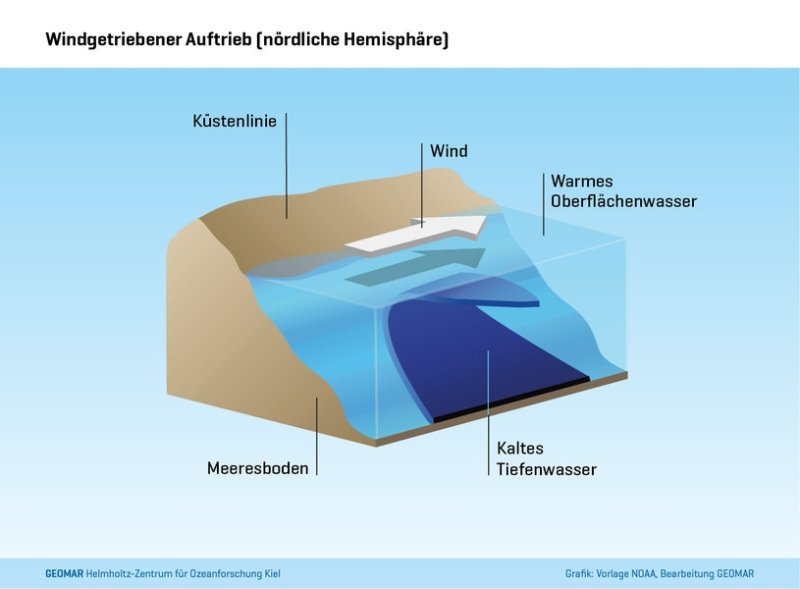
Function of coastal upwelling areas in the northern hemisphere, (c) NOAA / GEOMAR