New jellyfish species observed in the Kiel Canal
environmentmarine lifemarine conservationoceanecosystem
0 views - 0 viewers (visible to dev)
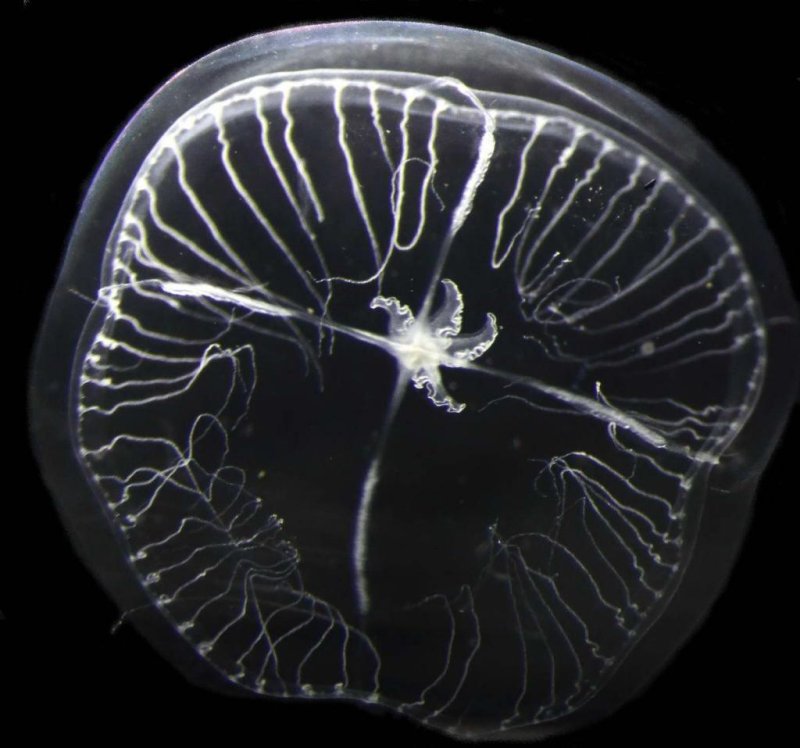
A specimen of the species Blackfordia virginica
(c) Cornelia Jaspers / GEOMAR, DTU Aqua (CC BY 4.0)
Further spread of Blackfordia virginica into the Baltic Sea is likely A new type of jellyfish has become established in the Kiel Canal. The brackish water-loving species Blackfordia virginica is a new player in the local ecosystem since summer 2016. This was the result of regular biological monitoring trips over the past ten years, which researchers from the GEOMAR Helmholtz Center for Ocean Research Kiel, the Technical University of Denmark and the University of Kiel have now published Global studies show that the number of species that migrate to foreign ecosystems is constantly increasing. While not all species can establish themselves in the new environments, successful bio-invaders have the potential to dramatically change their newly populated ecosystems. Also in the Baltic Sea numerous previously unknown species could be detected in the past decades. A prominent example is the American rib jellyfish Mnemiopsis leidyi , also called sea walnut. Scientists have now discovered in the evaluation of regular monitoring trips in the Kiel Canal and in the Baltic Sea another, for this region new jellyfish species: her professional name is Blackfordia virginica. Our long-term data show that this type of jellyfish has been established in the Kiel Canal since the summer of 2016 and is actively replicating, ie forming a new component of the ecosystem, " says Dr. Cornelia Jaspers, who works as a Biological Oceanographer at GEOMAR and DTU's National Institute of Aquatic Resources in Lyngby. The species Blackfordia virginica was first described in 1904 for the first time in the waters off the US state of Virginia. However, later studies suggest that it originally came from the Black Sea. " Meanwhile, she also finds herself in India, South America and South Africa. Since the 1970s, it has been occurring in brackish areas of northern France and, since the 1980s, in Portugal, " explains Dr. Jaspers. " So we're dealing with a species with a long history of success as a conqueror of alien ecosystems, where it can reach very large population densities. How the jellyfish got into the Kiel Canal is not exactly verifiable. Since the canal is the most heavily used artificial waterway in the world, ships have most likely brought in the jellyfish. Ballast water must not be pumped out in the canal. " That's why the jellyfish probably arrived here via jellyfish-polyps on ship hulls, which released young jellyfish, the so-called ephyrae, into the water, " Dr. Jaspers. Also outside the canal, in the Kiel fjord, the scientists could already prove the jellyfish. But there is no evidence that the species is actively replicating. " However, as part of our study, we have shown that the Baltic Sea, as a brackish water area, is an ideal habitat for Blackfordia virginica. We therefore expect further expansion ", Dr. Jaspers. What consequences this could have for the Baltic Sea is still unclear. From other regions it is known that Blackfordia virginica represents a significant competition to other plankton gullies. In addition, it can affect the offspring of fish species, because they eat their larvae. This could ultimately have economic consequences. Link to the study: https://doi.org/10.1186/s10152-018-0513-7

Additional data provided monitoring and training trips with the research vessel ALKOR in the Baltic Sea.
(c) Maike Nicolai / GEOMAR (CC BY 4.0)

Among other things, the study is based on samples and data obtained during regular monitoring trips with the research barge POLARFUCHS in the Kiel Canal
(c) Jan Steffen / GEOMAR (CC BY 4.0)