Magic nights of coral spawning
environmentmarine lifemarine conservationunderwater ecosystemcoral spawning
0 views - 0 viewers (visible to dev)
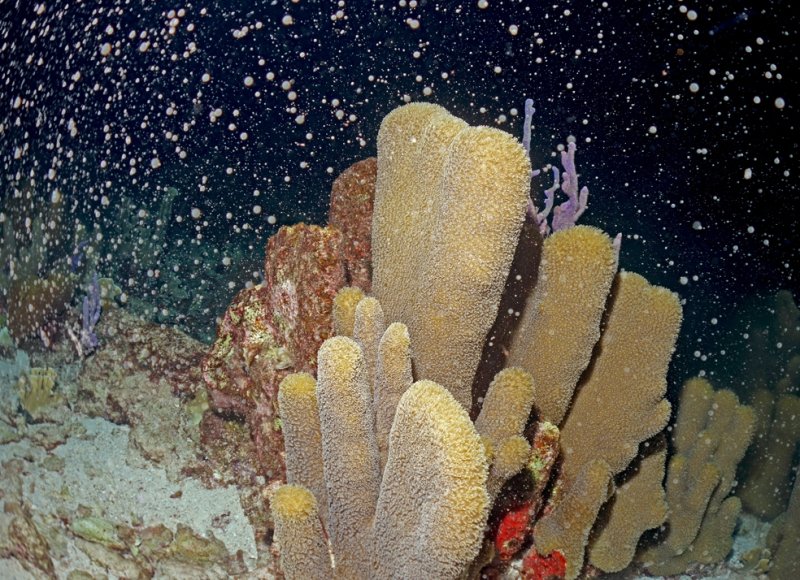

Coral spawning – diving in a 'snow storm' by Benjamin Mueller
On certain nights, around full moon, corals have their tryst of love. Diving on such a night is a lifetime experience and this is not overstated at all! Starting your dive, you are immediately aware of the crackling and rustling all around you. The reef bursts with activity, its origin somehow not detectable yet, but there is something in the wind―or rather in the water. It's gonna be a special night, the night of a coral mass spawning event; and many other creatures will join in.
Let's talk about coral sex!
Most stony corals―corals that build up the reef themselves with their calcareous structures―have developed a special strategy. Synchronized almost to the minute, corals of a certain species release their eggs and sperm into the water column where fertilization can take place. Led by the annual temperature profile to choose the right month, by the lunar cycle to appoint for the day, and by sunset time to pinpoint the hour, corals know exactly when it's time to start their lovegame.
Some coral species are hermaphrodites―having both sexes―and release eggs-and-sperm bundles. When the bundles are visible at each polyp's mouth, the coral prepares for spawning: they set. Then, sometimes the whole colony 'plops' out the tiny, pinkish, round bundles all together ( spawning video Montastrea annularis). For a moment they hang in the water, perfectly forming the shape of the coral before they start to drift away. Other corals are either female or male and they release egg-bundles or streaky clouds of sperm that turn the water milky ( spawning video Porites sp).
Often, several coral species spawn in concert, filling the water with gametes till you feel like diving within a snowstorm. And corals are not the only ones! Many other reef creatures take their chance to join the spawning night, such as sea fens, gorgonians, brittle stars, christmastree worms, and many more. The reason for that, as Sir Attenbourough repeatedly likes to emphasize in the famous Blue Planet series, is 'safety in numbers'. And this is a very thoughtful precaution! Predators, little swirling creatures like worms, crabs, shrimp, or fish, occupy the water to take part in the generously laid banquet and to get their piece of the high-protein goodies!
Not everywhere, coral spawning still happens. When corals suffer from stress―and being stressed out is a not uncommon state for corals these days―they are likely to stop their reproduction ( coral reefs are dying and are vulnerable to climate change). In other areas corals may still spawn, but there are factors that prevent the corals' enormous investment in offspring to pay off. The reasons are manifold: there may be too few colonies, too far apart to let fertilization of the gametes happen; water quality may be poor and coral larvae cannot develop; coral reef degradation and algae overgrowth may not spare the tiny coral larvae a place to settle and grow into a new coral colony. Times are rough for tiny coral babies (...and corals are important for survival of our planet).
Part of SECORE International's work is to raise sexually derived coral offspring where nature cannot carry out its duty on its own anymore. Especially when corals still spawn, but the number of new coral recruits is very low to non-existing. During night dives, we collect the coral gametes with nets (e.g. in Mexico) or, in the case of male corals releasing clouds of sperm, with syringes. We bring the gametes to the laboratory and let them fertilize. The delicate larvae are raised in various set ups, from perfectly-cared for, numerous, small bins for coral reproduction research to big bulk containers with thousands of larvae to study and apply restoration approaches. Like any living being, corals need to grow and reproduce. SECORE is giving them a helping hand in doing so ( SECORE's work).
SECORE.org
photos by Benjamin Mueller ( CARMABI ) and Paul Selvaggio ( Pittsburgh Zoo & PPG Aquarium
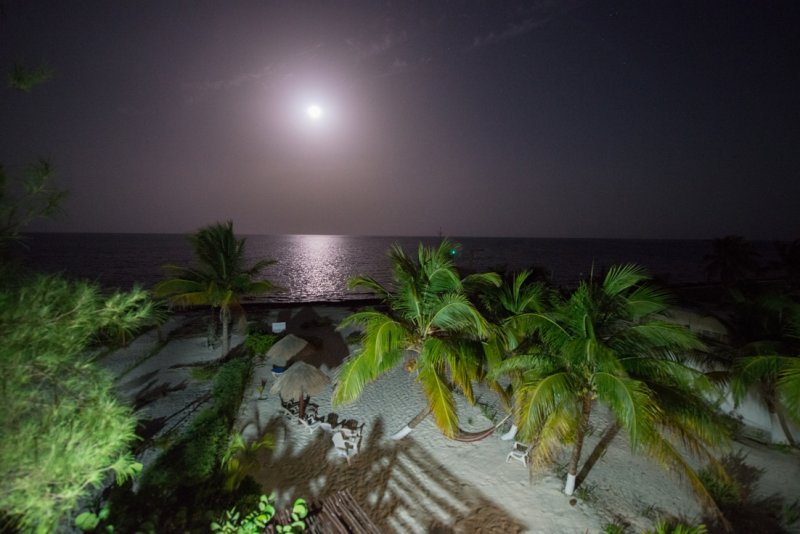

A corals love night, full moon over the Riviera Maya, Mexico by Paul Selvaggio
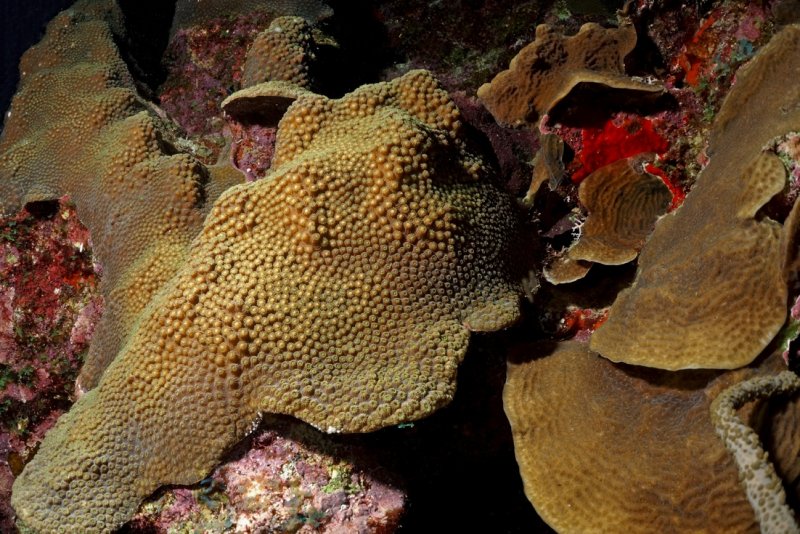

Massive coral setting for spawning by Benjamin Mueller
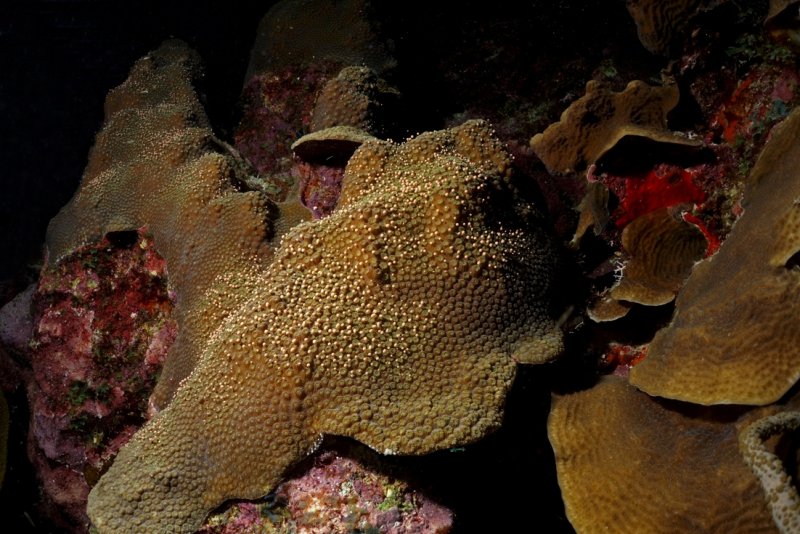

Same coral releasing egg-and-sperm bundles by Benjamin Mueller
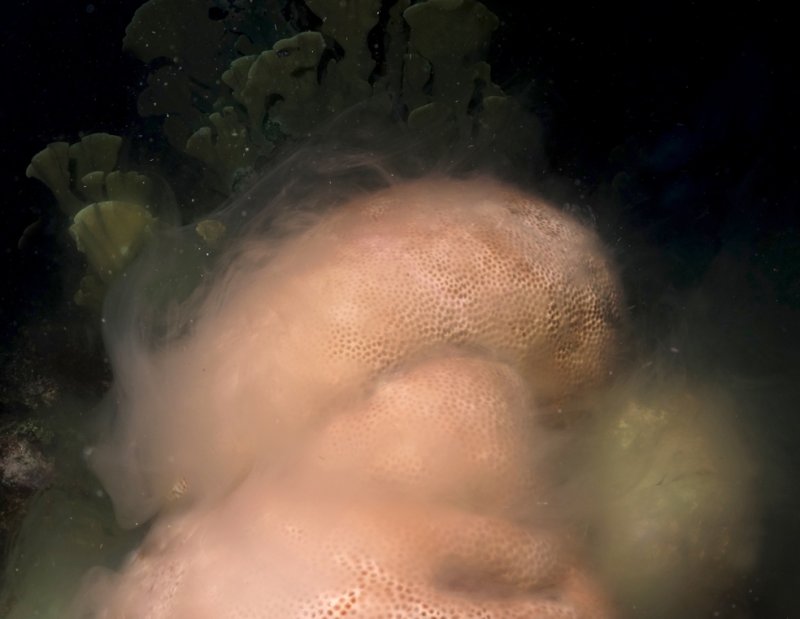
Male coral releasing milky clouds of sperm by Benjamin Mueller
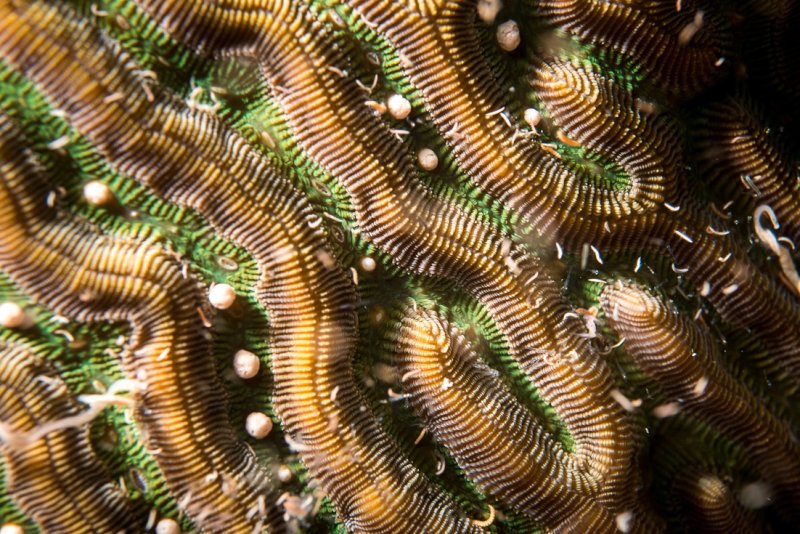

Close-up of spawning brain coral by Paul Selvaggio
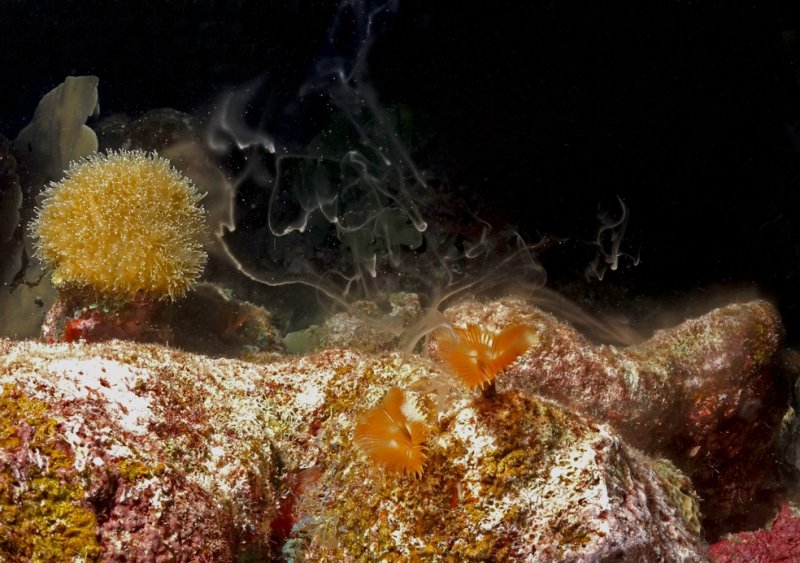

Spawning christmastree worms by Benjamin Mueller