Pacific coral reef keeps recovering from coral bleaching
environmentmarine conservationoceanclimate changecoral bleaching
0 views - 0 viewers (visible to dev)
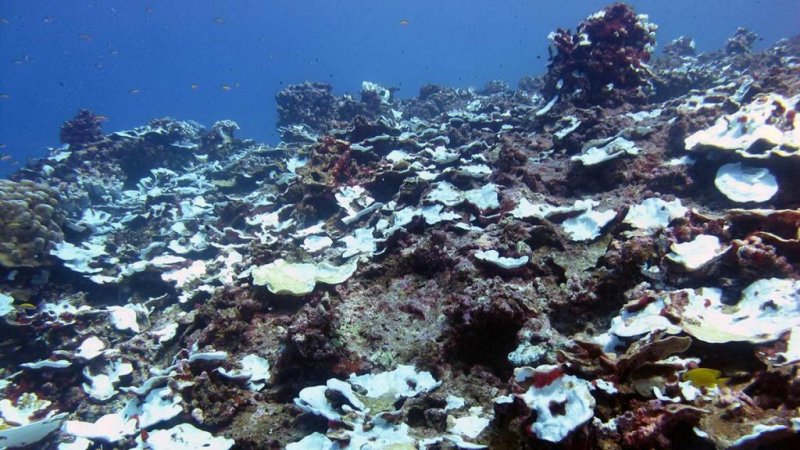

Ninety-five percent of the corals were bleached in November 2015, but still alive when the WHOI team visited Jarvis during the peak of El Nino's 2015-16.
(c) Thomas M. DeCarlo, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
Researchers prove historical bleaching events As climate change causes ocean temperatures to rise, coral reefs experience coral bleaching worldwide and die-offs. For many coral reefs, this is the first encounter with "extreme" temperature. For some reefs in the Central Pacific, however, the heat waves caused by El Nino are recurring events. How exactly these reefs react to repeated episodes of extreme heat was unclear. A recent study by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) revealed the history of bleaching on a reef in the epicentre of El Nino and showed how some corals recovered in extreme conditions. These huge marine heat waves, which are being exacerbated by global warming, are equivalent to an atomic bomb in terms of impact on coral reefs—they kill millions of corals across huge areas of ocean in a very short time," says WHOI researcher Anne Cohen. "We’ve seen this play out now globally for the past 30-40 years, and bleaching events have become more frequent and more severe When water temperatures rise slightly, symbiotic algae living in the cells of living corals begin to form toxic substances and are repelled by the corals. The algae usually provide the corals with food and energy and provide their bright colours. Without them, the corals seem to be "bleached" white, starving and dying. For their study, recently published in the journal Communications Biology, the research team travelled to Jarvis Island, a tiny, uninhabited island south of Hawaii to study the impact of the extreme climate on the corals. Jarvis is extremely secluded, part of a marine reserve and home to stunning coral reefs. Due to the location of the island in the middle of the Pacific, the coral reefs there experience extreme heat waves, which are caused by periodic El Nino events. The fact that Jarvis is right on the equator in the central Pacific puts this place at the centre of El Niño dynamics ," says NOAA researcher Hannah Barkley, lead author of the study. With no observational data on bleaching at the reef in Jarvis before 2015, Cohen and Barkley studied old corals that had lived on the reef for more than 100 years. They took core samples of the coral and created a kind of skeletal biopsy that records the history of the reef. After examining the cores on CT, they found evidence of several bleaching operations back to 1912, which had been preserved in the physical structure of the reef. The big old corals store 'stress bands' (a dense layer of calcium carbonate) in their skeletons during the heat spells, which appear clearly on the CT scan and reflect the historic heat waves, remembering past bleaching events on Jarvis in the corals. They can tell us what has been going on - even though we were not there to see for ourselves, " Cohen says. Jarvis has experienced above-average temperatures every four to seven years, going back over decades or even centuries. The team discovered that the reef was bleached hard during each heat wave, but seems to recover pretty quickly each time. The researchers see the main reason for the reef's recovery in the topography of the seabed in combination with the power of the trade winds. This leads to currents that bring cold, nutrient-rich water from the depths upwards. This nutrient-rich current nourishes fish and other aquatic creatures around the reef, which in turn eat algae that compete with the coral. They leave room for new, young coral polyps who eventually settle. According to the researchers the reefs around Jarvis are very resistant. The bleaching event in the course of the Super El Nino of 2015, however, was severe, the water temperatures higher than ever. The subsequent bleaching was the worst of all times: 95 percent of the coral of the island died. The big question for us is whether the reef will last, and even reefs like Jarvis, which have been recovering time and again, have a threshold," concludes Barkley. More Informationen: http://www.whoi.edu.
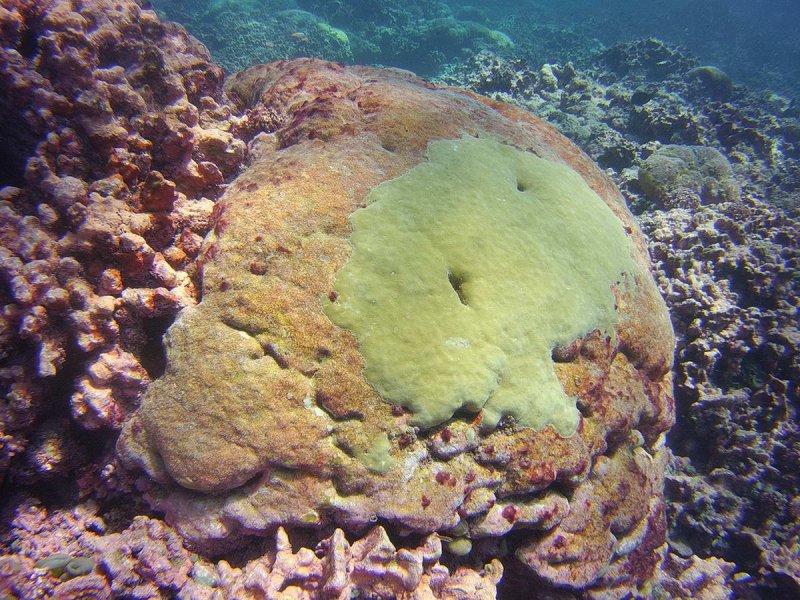

A very old Porites colony on Jarvis has seen many El Nino's. Extreme heat caused by the 2015-16 El Nino killed a significant portion of the coral tissue, but some remained alive, and had started to grow back, green and healthy, by 2016.
(c) Hannah Barkley, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
Coral cores waiting to be CAT scanned at WHOI.
(c) Thomas M. DeCarlo, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
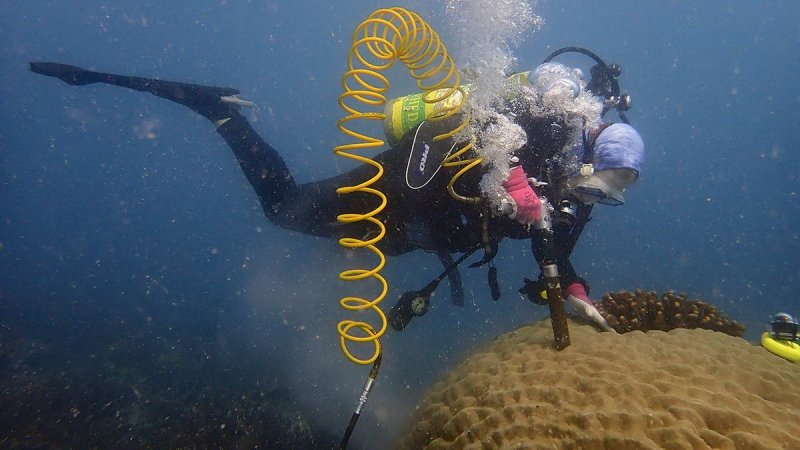

Hannah Barkley extracts a core from a massive Porites colony. The core