Sicily: Southeast flank of Mount Etna is sliding
environmentmount etnatsunami threatmarine geodesyunderwater monitoring
0 views - 0 viewers (visible to dev)
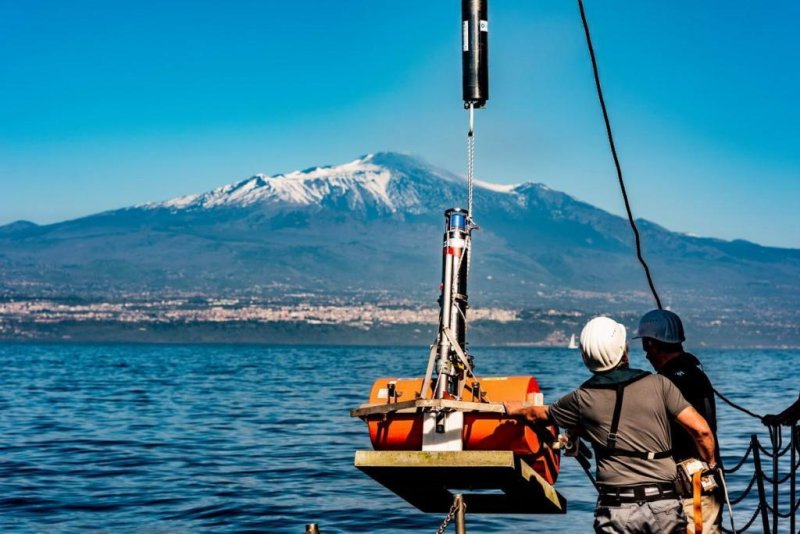

The GeoSEA transponders have been dropped off on the eastern flank of Mount Etna from the research vessel "POSEIDON", photo: © Felix Gross (CC BY 4.0)
Volcanic flank moves underwater – an upcoming tsunami threat? The southeast flank of Mount Etna slowly slips towards the sea. A team from the GEOMAR Helmholtz Center for Ocean Research Kiel and the Cluster of Excellence "Ocean of the Future" was able to prove with a new, sound-based surveying network that the slope continues to move under water. Within eight days he moved about four centimetres. A sudden and rapid slippage of the entire slope could lead to a tsunami with serious consequences for the entire region The most active volcano in Europe, the Etna is closely monitored by science and the authorities. Meanwhile, satellite-based measurements have been showing for some time that the southeast slope of the volcano is slipping slowly towards the sea, while the other parts of Mount Etna are stable. Until now, it was unclear whether the movement will continue under water, as measurements by satellite or GPS are not possible there. Using a novel surveying network, which is part of the GEOMAR GeoSEA array, scientists from GEOMAR, the Kiel University of Kiel, with a focus on marine science, and the National Geophysical and Vulcanological Institute (INGV) have now been able for the first time to study the movement of the slope in horizontal and vertical direction. The results of the study were recently published in the international journal Science Advances. At Mount Etna, we used the sound-based survey under water, the so-called marine geodesy, on a volcano, for the first time " explains Dr. med. Morelia Urlaub, lead author of the study. She led the investigations within the project "MAGOMET - Marine geodesy for offshore monitoring of Mount Etna". The GEOMAR team placed a total of five transponder measurement stations along the fault line, which marks the boundary between a slipping edge and a stable slope, in April 2016 - we reported We placed three on the sliding area, two on the other side – the stable side - of the fault line, " said Urlaub. The transponders then sent an audible signal every 90 minutes. Since the speed of sound under water is known, relative movements of the seabed can be determined centimetre-accurate over the period of time that the signal is travelling. " We clearly noted that in May 2017, the slope slid four centimetres towards the sea in eight days, sinking an inch, " says Urlaub. This movement can be compared with a slow earthquake, a so-called "slow slip". It was the first time that the horizontal movement of such a slow-slip event was detected underwater. Overall, the system was in use for around 15 months. Compared with data obtained by satellite, it was found that the southeast slope has moved similarly far ashore over the same period. "The entire south-eastern slope has changed its position," says Dr. Vacation. All in all, our results suggest that the slope is slipping due to gravity rather than because of the rise of magma, " she continues. If magma were to trigger the movement in the centre of the volcano, the slope would show a much stronger movement on land than under water. This insight is important for further risk assessment. " The entire slope is in motion due to gravity. Therefore, it is quite possible that it will suddenly slip off, which could trigger a tsunami in the entire Mediterranean, " said Professor Heidrun Kopp, coordinator of the GeoSEA array and co-author of the study. However, it is not possible to predict by the test results whether and when this event might occur. Link to the study: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aat9700

The research vessel "POSEIDON" off Mount Etna, photo: © Felix Gross (CC BY 4.0)
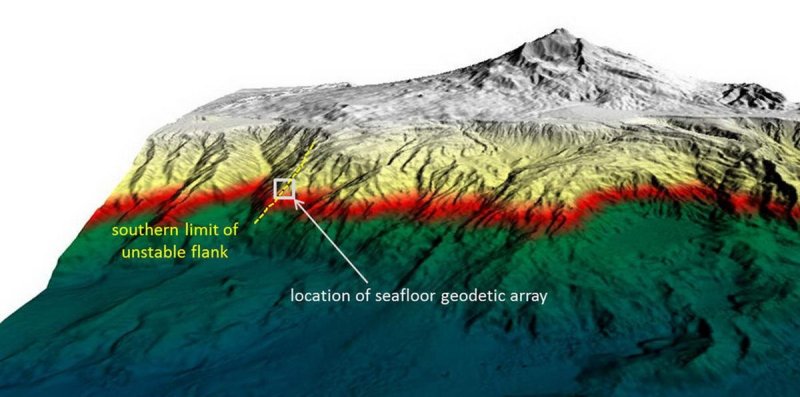
3D view of the Etna east flank with the position of the GeoSEA monitoring network, graphics: © Morelia Urlaub / Felix Gross